Maintaining a fast and performant website that can work in multiple environments, slow internet, and devices is such a hard thing to do, and you may have struggled with this thing called Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), which all it does is tell every single time that there is an item on your page that is not rendering/loading as fast as it was expecting, which is obnoxious. In this blog post, you'll what exactly is LCP and how each of its 4 components works together to give you bad results. Which is probably the reason why you're not ranking well.
What is LCP
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) is a key web performance
metric that measures the time it takes for the largest content element visible
in the viewport to render on a web page. This element is typically an image,
video, or large text block. LCP is one of Google's Core Web Vitals, used to
assess website performance and user experience.
LCP focuses on the content above the fold, which is visible
without scrolling. It provides insight into a website's perceived loading speed by measuring the render time of the most visually significant
element. This metric is considered more reliable than First Contentful Paint
(FCP) for determining when a page is ready for interaction.
To provide a good user experience:
- LCP
should occur within 2.5 seconds of page load initiation (considered good).
- LCP
between 2.5 and 4 seconds needs improvement.
- LCP
above 4 seconds is considered poor.
Optimizing LCP can improve a website's overall user experience and lead to higher search rankings, lower bounce rates, and increased conversion rates.
Now LCP has different components that lead to it, for example:
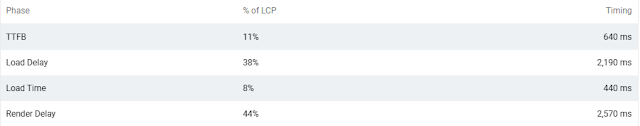
Time to First Byte (TTFB)
TTFB measures the time between the request for a resource and when the first byte of the response begins to arrive. It includes:
- Redirect time
- Service worker startup time
- DNS lookup
- Connection and TLS negotiation
- Initial server response time
Load Delay
Load delay (Resource Load Delay) is the time between TTFB and when the browser starts loading the LCP resource. Key characteristics include:
- The time between the HTML document starts loading and the image download
- Directly impacts LCP performance
- Determines initial resource loading speed
Render Delay
Render delay is the time between LCP resource loading and full element rendering. Caused by:
- Render-blocking resources
- Elements not yet in the DOM
- Hidden elements by code
- Main thread blockage
Ideal render delay: About 10% of the total LCP budget
Attention: I noticed that when I start the analyzing in the lighthouse, if I was not on the page while analyzing the performance score will go down significantly, and some of the factors to LCP will go wild, like Load Time and Render Delay. So keep this on a good note :).
 |
| Not on the page |
Load Time
Load time refers to the duration to load the LCP resource, also known as Resource Load Duration.
- For text nodes with system fonts: 0 load time
- Measures actual resource download duration
Relationship to LCP
These components collectively compose the Largest Contentful Paint metric:
- TTFB: Initial process delay
- Load Delay: The time until the Resource starts loading
- Load Time: time taken for the element to be fully loaded
- Render Delay: Element display time
Optimization Impact
Improving these components can:
- Enhance user experience
- Boost search engine rankings
- Reduce perceived loading time
Total LCP Time = TTFB + Load Delay + Load Time + Render Delay
Thank you for reading


0 comments:
Post a Comment